|
Pakistan
The
Islamic Republic of Pakistan is situated in
South Asia, the seat of one of the earliest
known civilizations "the Indus valley
civilization". It lies between latitudes 24 and
37 degrees North and longitudes 62 and 75
degrees east covering a total land area of 6,774
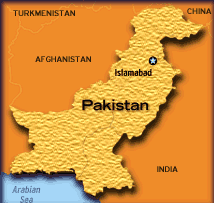
km. Pakistan shares its
 borders
with Iran on the west, India in the southeast,
Afghanistan in the north-west, and China in the
north. The Arabian Sea lies to its south. It has
the world's second highest mountain, the K2. borders
with Iran on the west, India in the southeast,
Afghanistan in the north-west, and China in the
north. The Arabian Sea lies to its south. It has
the world's second highest mountain, the K2.
Pakistan is a land of
great topographic and climatic contrasts. It is
geographically divided into three areas: the
northern highlands, the Indus river plains and
the Baluchistan plateau. Pakistan has four
seasons, winter, spring, summer and winter. The
monsoons are between July and August
Vulnerability to Natural Hazards:
Pakistan is vulnerable to
most of the natural hazards. It is prone to
floods, earthquakes, droughts, cyclonic storms,
locust invasion and epidemics. Being densely
populated the impact of these natural phenomenon
is felt more.
Floods:
Floods are by far the
most frequent. It occurs during the monsoon
period of July to September due to heavy rain in
the plains and the catchment area of the rivers.
With the swelling of the rivers heavy flooding
occurs causing great destruction to lives and
livelihoods.
Earthquakes:
Pakistan lies in the
seismic belt and therefore suffers from frequent
earthquakes of smaller magnitudes. The
devastation is immense because of the poor
quality of buildings.
Locust Invasion:
Pakistan lies in the
seismic belt and therefore suffers from frequent
earthquakes of smaller magnitudes. The
devastation is immense because of the poor
quality of buildings.
Links:
|

